A bacterial condition known as gonorrhoea is infectious and has been around for a very long time. It’s estimated that more than 350,000 people are infected with gonorrhea annually in the United States. The infection rate has increased 5 percent since 2013, a rise believed to be due to greater infection rates among gay and bisexual men.
You can have gonorrhea without any obvious symptoms, especially if you’re a woman. If any symptoms are noticeable, they generally occur within 2 to 10 days of infection. Gonorrhea is spread by direct contact with infected mucous membranes in the genitals, rectum, and throat. In women, the bacteria typically infect the cervix (the opening of the uterus), which becomes tender to the touch and inflamed. In about 15 percent of infected women, the infection travels to the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries (this is known as pelvic inflammatory disease). Men are usually infected first in the urethra, the tube that urine and sperm pass through.
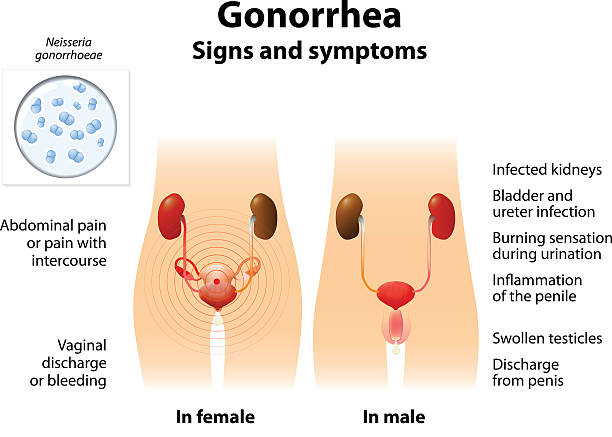
Table of Contents
Symptoms of gonorrhea
• Painful urination
• Green-yellow vaginal or penile discharge
• Sore throat (if contracted through oral sex)—though many people with throat infections have no symptoms or signs
• Rectal pain, soreness, bleeding, or discharge (if contracted through anal sex)
What causes gonnorhea?
Gonorrhea is caused by a bacterium, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, that can grow rapidly on the body’s mucous membranes. The infection is spread by sexual contact (vaginal, anal, or oral). A baby can contract gonorrhea from an infected pregnant mother during childbirth, which may cause the infant to go blind unless promptly treated.
What if you do nothing?
Gonorrhea may be both chronic and progressive. If left untreated, it can result in arthritis, skin sores, and heart or brain infection. Pelvic inflammatory disease can cause chronic pelvic pain and may also damage fallopian tubes, leading to ectopic pregnancy (potentially fatal to the mother) and infertility. Gonorrhoea in males can damage the prostate and cause urethral scarring, which makes urinating challenging. Gonorrhea can also cause permanent sterility in women, and it can facilitate the transmission of HIV, the virus that causes AIDS. Infants born to infected mothers are at risk of becoming blind unless treated. All newborns have an antibacterial medication put on their eyes at birth to prevent this.
Also Read:
- Sexually Transmitted Disease
- The Real Symptoms of AIDS
- Women’s Health: A Perception
- 10 Health Benefits of Daily Sex
- 7 Ways Yoga For Better Sex
Are there any home remedies for gonorrhea?
Gonorrhea cannot be accurately diagnosed and treated without professional help. There are no home remedies, so see a doctor or another health-care professional if you get infected or think you might be infected. You should abstain from sexual intercourse until your physician is sure the infection is completely cured.
How to prevent gonorrhea
- Know your partner. Get to know your sex partner before becoming intimate. Avoid anyone whose health status is questionable. Reducing your number of sex partners also reduces the risk.
- Use a condom. Latex condoms effectively prevent the spread of gonorrhea.
- Detect it early. If you notice any symptoms, avoid sexual contact and see your physician or other health-care provider immediately. Also notify all of your recent sex partners so that they can get tested and receive treatment, if necessary.
- Get tested routinely if you are at high risk. Individuals at high risk include young women (under the age of 25) who are sexually active; both men and women with a history of repeated episodes of gonorrhea; and men who have sex with men. Also, be sure to get tested if you become pregnant and have had multiple sex partners.
When to call your doctor
Contact your physician immediately if you have any of the symptoms of gonorrhea listed above or if you learn that a sex partner has gonorrhea.
What your doctor will do
Following a thorough examination, your physician will diagnose the ailment with a nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT) of a urine specimen (men and women) or vaginal specimen (women). This test identifies the DNA of the bacterium that causes gonorrhea and is considered the test of choice.
If the test confirms you have gonorrhea, you’re likely to receive two antibiotics: ceftriaxone (Rocephin) and azithromycin (Zithromax). These are now prescribed in combination due to the increasing prevalence of drug-resistant bacteria. According to the CDC, people treated for gonorrhea should abstain from sexual activity for 7 days after receiving treatment and until all sex partners are adequately treated (7 days following therapy and the disappearance of symptoms, if any). Any person who receives a diagnosis of gonorrhea should be tested for other STDs, including chlamydia, syphilis, and HIV.
For more information: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention




